Collagen supplements are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). That said, some people have reported side effects when consuming collagen peptides. So, does that mean you should abandon the bottle of collagen powder in your pantry?
Not really. Ahead, we explain potential collagen peptides' side effects to help you understand why some people experience them while others don’t. It’s all about consuming the right amount and scrutinizing the ingredient list.
What Are the Side Effects of Taking Collagen?
From an upset stomach to disrupted sleep, these are the common side effects of collagen peptides to look out for. Spoiler alert: Most of these adverse reactions usually occur with collagen overconsumption.
1. Digestive Discomfort
Digestive discomfort is perhaps the most common side effect that the average person experiences with collagen supplements.
A 2000 clinical trial published in the Journal of Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism reported mild gastrointestinal symptoms like bloatedness. Other anecdotal accounts include heartburn, gas, constipation, and diarrhea.
The good news is that these digestive problems typically happen after eating gelatin rather than collagen peptides. Unlike gelatin that’s partially hydrolyzed, collagen peptides are fully hydrolyzed (aka hydrolyzed collagen). The latter’s small molecular weight makes them highly bioavailable in the human body, which is science-speak for more efficient digestion and absorption. Plus, science suggests that collagen peptides may improve your overall gut health.
If you still struggle with stomach issues after consuming collagen peptides, it could be due to other ingredients in the supplement’s composition rather than the collagen itself. Steer clear of synthetic substances like fillers, additives, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and sweeteners.
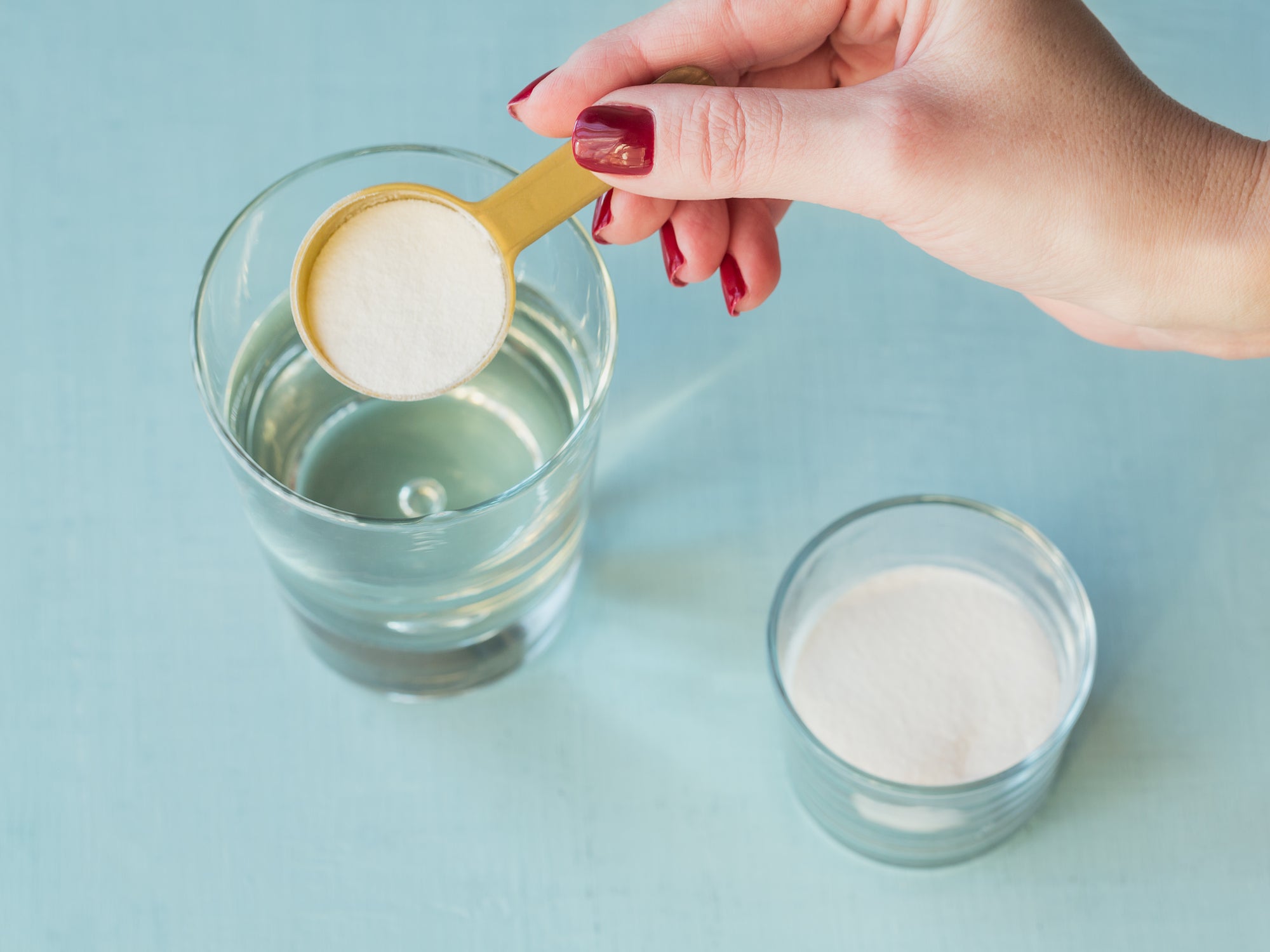
To downplay the odds of gastrointestinal discomfort, look for collagen peptides supplements with a relatively clean ingredient list. For that reason, you may want to try Zen Principle’s Beef Collagen Peptides Powder and Marine Collagen Peptides Powder. (Not sure which collagen supplement to go for? Check out our comparison guide on “Marine Collagen vs Grass-Fed Beef Collagen.”)
2. A Bad Taste
The last thing you want is collagen peptides to leave a bad taste in your mouth. Unfortunately, that’s what some people experience, per the earlier 2000 study.
This could be due to the animal source from which the collagen is extracted. Most supplements come from cows, fish, shellfish, and pigs. As such, lower-quality collagen peptides may come with a “beefy” or “fishy” flavor.
Other substances on the ingredient list may also be the culprit behind the unpleasant taste. Some manufacturers add artificial flavorings and sweeteners to try and make the supplement taste better. Unfortunately, these cloyingly sweet synthetics may be why the collagen peptides don’t agree with your taste buds.
Your best bet is to choose unflavored collagen peptides (yes, they exist!). Case in point: Zen Principle’s Beef Collagen Peptides Powder and Marine Collagen Peptides Powder. Because they are unflavored, adding them to your food and drinks is unlikely to ruin your meals.
3. Food sensitivities and allergies
As mentioned earlier, many collagen supplements are extracted from bovine, marine, and porcine sources. Some supplements also include additional nutrients like herbs and superfoods.
Before you add collagen peptides to your diet, always check the ingredient list first. This way, you can head off any potential food sensitivities and allergies.
4. Headache

Consuming collagen peptides may cause headaches in some people, but this is not a common side effect.
Science explained that elevated levels of glutamic acid can result in a throbbing head. Given that glutamic acid is one of the amino acids present in the collagen protein, eating too many collagen peptides may indirectly lead to an unwanted headache.
5. Poor Mood and Sleep
Collagen is an incomplete protein as it does not contain tryptophan, one of the nine essential amino acids the human body needs.
Relegating too much of your protein intake to collagen sources means you run the risk of not consuming enough tryptophan. Unfortunately, tryptophan deficiency is known to dampen your mood and disrupt your sleep.
According to a 2012 review in the Journal of Nutrition, tryptophan is needed to synthesize serotonin and melatonin. Given that serotonin is the “feel-good” brain chemical that regulates your mood, it’s no wonder that “tryptophan deficiency increases anxiety and irritability.”
Meanwhile, reduced tryptophan levels may indirectly impact your sleep-wake cycle due to a shortfall of the sleep-promoting hormone, melatonin. Ample scientific evidence shows that melatonin deficiency is associated with poor sleep efficiency, insomnia, and other sleep disorders.
What Are the Symptoms of Too Much Collagen?
Believe it or not, it’s possible to consume too many collagen peptides.
The resulting side effects of excessive collagen consumption include:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Increased risk of kidney stone formation
- Dangerously high calcium levels
You can read about each of these collagen peptides' side effects in our post on “What are the symptoms of taking too much collagen?”
Consume Collagen in Moderation
Many of the side effects of collagen peptides are usually due to overconsumption. In this case, you can easily avoid these negative consequences by moderating your collagen intake. Follow the recommended dosage guidelines on the product packaging and consult a licensed healthcare provider if necessary.
To mitigate other side effects such as a bad aftertaste and food allergies, fine-comb the ingredient list. Prioritize brands that sell top-quality, clean supplements and stay away from specific foods your digestive system doesn’t agree with.
All in all, the benefits of collagen peptides outweigh their potential side effects, so it’s still in your best interest to keep these supplements in your everyday diet.






6 comments
Hi, i am having daily 2 scoops of collagen in my coffe and i would like to know if uninterrupted collagen is bad for my body, thank you